Benefits from evaluation of condition
and strength of the structure
Evaluation of condition and strength of
the structure is done in order to know about condition
of the structure as well as deterioration, defects,
damages, and load carrying capacities (safety limit
in carrying loads) of the structure. However, it might
be done to collect data for making decision on repair,
improvement or retrofit of the structure as well as
to gather information for structural analysis, engineering
calculation, and designing of structural repair or improvement.
Schemes for evaluation of condition
and strength of the structure
Schemes for evaluation of condition and strength
of the structure might be categorized roughly as follows.
- Searching for sign of deterioration
and damages that occur with the material itself and
different members of the structure such as cracks, porosity,
defects, inclination, settlement, and movement.
- Define tendency of having damages in the future such
as measuring acidity and alkalinity inside the material,
measuring electrical potential difference of different
parts of the structure, measuring density of the material,
inspecting connection pattern of members of the structure.
- Examine responses of different parts of the structure
to different patterns of applied forces or different
types of stimulation. This will give a broad view on
condition and status of the structure. This might be
done by measuring forces and movements when carrying
some specific load or under normal service condition.
- Comparing key parameters of the structure at different
times to observe change in general condition of the
structure (which will cause change in values of key
parameters). Key parameters must be selected carefully
so that they can really reflect deterioration of the
structure.
Cause of structural deterioration
and damages
Generally, structure of a building, bridge,
dam, etc. will be designed to have the maximum capacity
in carrying loads at a certain level for some certain
service period. That period can be taken as life of
the structure. In the case of buildings, that period
can be called life of the building. Likewise, it will
be called life of the bridge in the case of bridges.
Limited service life of a structure is mainly caused
by deterioration and damage of construction materials.
Deterioration and damage may come from corrosion, fatigue
(when load was sustained for a long time or repeated
for many cycles), overloading, loading pattern unaccounted
for in the design, or chemical degradation. Many factors
from surrounding environment like acidity, salt, humidity,
and change of ambient temperature also cause deterioration.
Earthquake, fire, storm or other kinds of hazardous event that
causes damage to the structure may seriously reduce
life of the structure.
If analysis, calculation, and design were carried
out correctly and properly together with good construction
by means of good material, workmanship, equipment and
regular maintenance of the structure, the structure
will be able to carry the specified maximum load throughout
its entire life. Maximum level for a load pattern may
be different from those allowed for other load patterns;
such as maximum level for a force applied in one direction
may not be the same as that allowed for a force applied
in another direction.
In conclusion, deterioration of the structure begins
since it was constructed and this results in continuous
reduction of strength and load carrying capacity of
the structure until it is unsafe to use the structure.
Repair, retrofit, or strengthening of the structure
when there is a sign of deterioration or
damage in some part of the structure will help to prevent
spreading of the damage to other parts and will considerably
prolong life of the structure. Repair, retrofit or strengthening
of the structure in the early stage when deterioration
and damage is still small will cost much less than doing
it when damage already spreads.
|
|

Bond test of concrete

Measure deflection of structural members when carrying
the load

Measure forces in members of the bridge loaded by using
the test locomotive
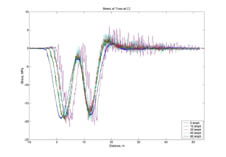
Force occouring inside the member from
measurement
|
